Our Proposal
Conserving Our Glaciers to Combat Climate Change
Glacier Dam is a paradigm shift in geoengineering. A product that will extend the life of glaciers and minimize risk to fragile frozen ecosystems by replicating what is already happening in nature.
Glacier Dam is a cost effective solution targeting one of the major effects of climate change — glaciers melting. If we can extend the life of glaciers, this will help to:
Reflect more solar radiation away (and preserve what reflection we have) to decelerate runaway global temperatures
Slow the rise of ocean-levels
Provide water security for billions of people relying on melt water
Preserve the cryosphere
We are losing the climate battle when glaciers are in retreat
Glaciers, across the board, are receding at an accelerated rate. This spells danger for the cryosphere. The cryosphere is made up of all the frozen water on the earth’s surface, and accounts for two thirds of the world’s fresh water reserves. These frozen places include far more than the polar regions, stretching from Mt. Kilimanjaro in Africa to the frozen lakes of the USA, and anywhere else with water in solid form.
Frozen water reflects the sun’s radiation better than any other surface on the planet. When glaciers are receding there is less white surface area to bounce the sun’s rays back into space (known as albedo). Our planet then absorbs more of the sun’s energy and global temperatures rise even more quickly.
How are glaciers melting?
As glacial ice flows downward, it reaches warmer climates or the ocean. This triggers various processes that cause the glacier to lose mass. The top two factors are:
Surface melt, including evaporation.
Calving/break offs, which occur when ice from the foot of a glacier breaks off. Ice chunks of all shapes and sizes float downstream, diminishing the glacier’s overall structural integrity. Calving is even more critical to tidewater glaciers (that is, glaciers terminating in the oceans and other tidal bodies of water through fjords or ice shelves), as they account for 70% of global ice loss to the ocean. This causes a chain reaction that speeds up the downward flow of glaciers, because an imbalance is created whereby the top of the glacier gains mass by precipitation while significant loss occurs at the foot. The faster glaciers flow, the more glaciers melt.
Glacier Dam: Following in Nature's Footsteps
Sometimes, nature forms its own glacier dams. Ice break offs can be blocked by a narrowing river, and in some cases, the break offs have the chance to gather and pack in until they refreeze into a new glacier.
With Glacier Dam, it is possible to bring the "narrowing river" effect closer to the foot of the glacier. This means the break offs refreeze to the foot of the glacier. The glacier then regenerates by growing across the frozen surfaces.
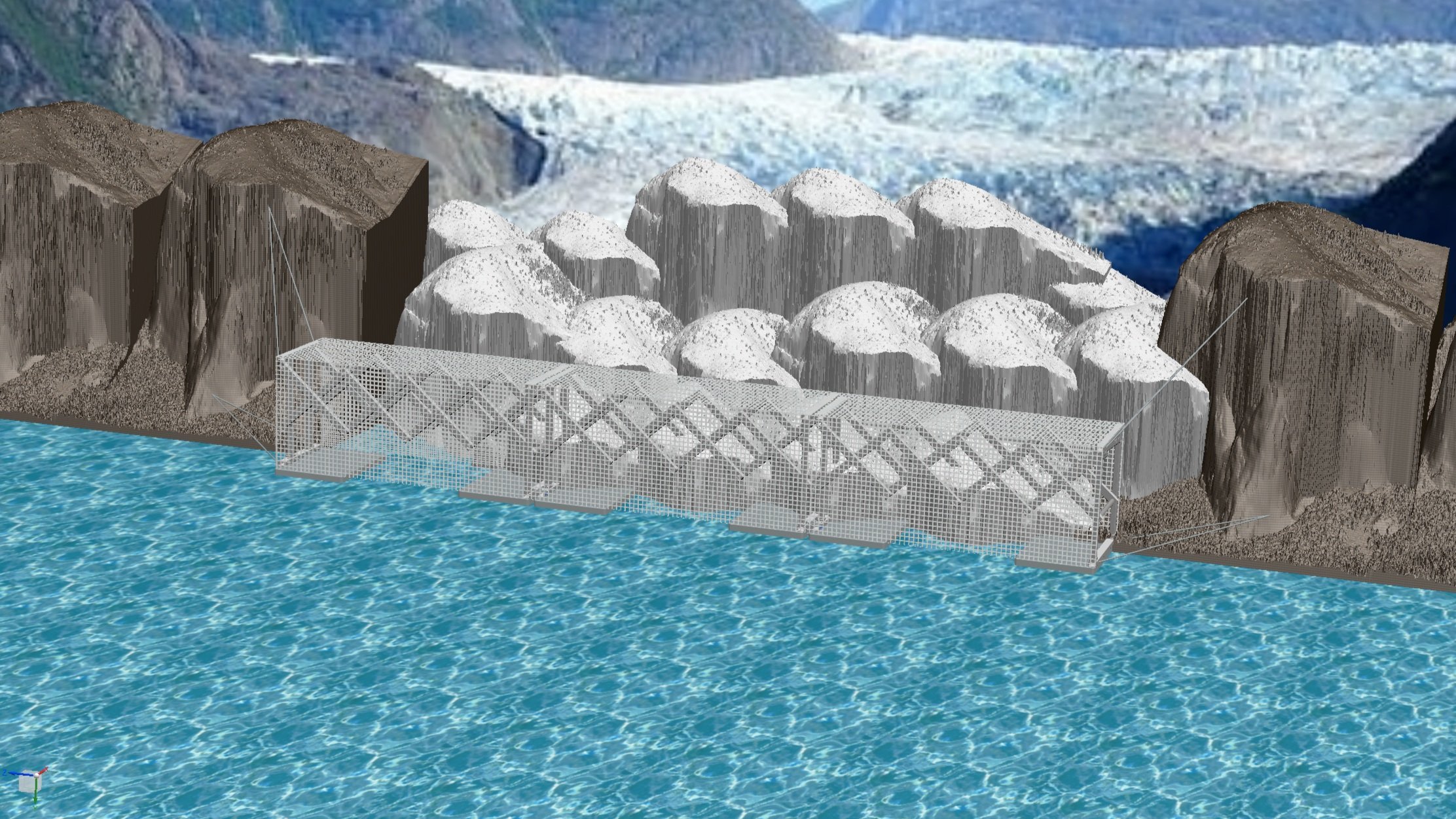
Glacier Dam: How it works
Glacier Dam is not just a regular dam.
Glacier Dam functions by blocking ice break offs from floating away while allowing the free flow of water. Then, as the dam and breakoffs freeze into an ice wall, the space between the dam and the glacier is filled with slushy water and an ice mixture, called mélange. This mélange helps to refreeze break offs to the main body of the glacier, allowing the glacier to advance.
By reducing the rate of glacier melt, this allows the glacier front to thicken. Once the ice growth on the Glacier Dam begins to accumulate and strengthen, it forms a strong anchor to the retreating glacial front.
Glacier Dam is modular and collapsible, for ease of transportation and implementation. It is designed to be flexible to site-specific conditions and assembled on-site. It will be built from carbon neutral and negative materials with insulative properties and high compressive strength.
The most important milestone in large-scale deployment is restoration of small, calving glaciers. Then, we aim to scale up to bigger, retreating glaciers.
Using satellite data allows us to choose the smartest place to deploy Glacier Dam to block the most exits and prevent the largest amount of break offs going downstream. Our goal is to have the minimum number of Glacier Dams for the maximum impact.
Glacier Dam in action
Glacier Dam reestablishes the foot of the glacier. Once the foot of the glacier holds strong, it acts as a speed bump to slow the glacier’s flow. The slower the glacier flows, the lower the rate of melting and break offs. Through satellite data, we will measure the speed of the glacier’s flow to track Glacier Dam’s progress.
Planning ahead for long term success
Using satellite data, we can create computer models of multiple exits of the same glacier. This allows us to choose the most strategic place to deploy Glacier Dam that will block the most exits,and prevent the largest amount of break offs from flowing downstream. Our goal is to deploy the minimum amount of Glacier Dams for maximum impact, including repeated Glacier Dams downstream for compounded advancement of the glacier.
How you can support Glacier Dam?
We are a team of dedicated glaciologists, engineers, and data scientists who are passionate about the environment and wish to provide a service to the global community.
We see the time to act is now to tackle climate change. Our belief is that Glacier Dam is a crucial step toward decelerating rapid glacier melt.
We invite you to support us on this journey.
Contribute to Glacier Dam now.
Get Involved!
Become a partner today to help mitigate impacts of climate change.